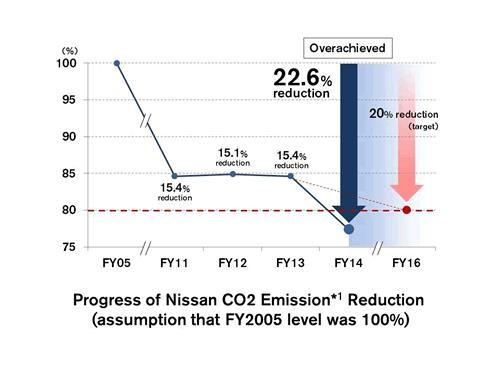
Nissan global corporate activities reduce CO2 emissions by 22.6 percent
Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. made great strides in reducing CO2 emissions and improving sustainability in its global corporate activities in fiscal year 2014 while simultaneously increasing vehicle production and plant energy efficiency. The company achieved a 22.6 percent cut in CO2 when compared to fiscal year 2005, thus achieving its goal to reduce CO2 emissions from corporate activities by 20 percent during that period.
Nissan continues to work toward achieving its environmental targets set forth in the company’s action plan, Nissan Green Program 2016 (NGP2016), through a number of innovative sustainability initiatives in following key areas:
Corporate carbon footprint minimization
One of Nissan’s CO2 emission goals is to increase the usage rate of renewable energy in its global business activities to nine percent by fiscal year 2016. Nissan is utilizing a number of proven forms of sustainable energy generation to help minimize its corporate carbon footprint. One example of this is Nissan Mexico’s Aguascalientes A1 Plant, which has manufactured 500,000 vehicles through the use of clean energies, making it the first automotive company in Mexico, as well as the first manufacturing facility of the Renault-Nissan Alliance, to achieve this milestone. Through the use of renewable energy, Nissan Mexicana has prevented 152,800 tons of CO2 from entering the atmosphere, and has so far assembled 460,000 vehicles with wind power and 57,400 vehicles with biogas power from the city’s landfills. In all, the use of clean energies accounted for an astounding 68 percent of the production at the Aguascalientes A1 Plant.
The Nissan Energy Saving Collaboration (NESCO) conducts annual surveys (starting 2003 in Japan and 2013 in Europe, Mexico and China) to measure energy loss at Nissan plants in order to develop ongoing new energy-saving countermeasures. NESCO specializes in controlling energy consumption, and diagnoses and visualizes energy flow and its inefficiencies. For example, NESCO studies iron forging, casting and paint shops, then proposes measures to plant management on how to prevent energy loss. In fiscal year 2014, NESCO proposed solutions to reduce CO2 emissions by 50,000 tons.
NESCO has also been used at five Renault and Alliance plants, including AVTOVAZ, UAG and RSM, which have already seen excellent results. NESCO’s area of focus will expand to include waste water loss and waste reduction, in addition to energy loss and CO2 reduction.
Zero emission vehicle penetration
Nissan is improving sustainable mobility through the widespread use of zero emission vehicles. The Nissan LEAF electric vehicle has the ability to safely and conveniently supply electricity stored within its high-capacity lithium-ion batteries to a home through the LEAF to Home power supply system. In addition, Nissan’s “No Charge to Charge” program in the United States provides free access to selected charging stations for two years with the lease or purchase of a new Nissan LEAF in numerous cities including Los Angeles, Portland, San Francisco and Seattle.
In 2014, the company further expanded zero-emission mobility with the introduction of the e-NV200 in the European and Japanese markets. The versatile e-NV200, like the LEAF, has the potential to be used as a mobile power source. In China, the Dongfeng Nissan Passenger Vehicle Company, a division of Nissan’s joint venture with Dongfeng Motor Company, launched the Venucia e30 electric vehicle that offers Chinese consumers a fun-to-drive and reliable EV with very affordable operating costs.
The Nissan Green Program 2016 (NGP2016), launched in fiscal year 2011, is guiding Nissan’s efforts to reduce the company’s environmental impact and resource consumption from global corporate activities while advancing ecological harmony. The company is dedicated to improving in four main areas: zero-emission vehicle penetration, fuel-efficient vehicle expansion, corporate carbon footprint minimization and new natural resource use minimization.
Nissan continues to work toward achieving its environmental targets set forth in the company’s action plan, Nissan Green Program 2016 (NGP2016), through a number of innovative sustainability initiatives in following key areas:
Corporate carbon footprint minimization
One of Nissan’s CO2 emission goals is to increase the usage rate of renewable energy in its global business activities to nine percent by fiscal year 2016. Nissan is utilizing a number of proven forms of sustainable energy generation to help minimize its corporate carbon footprint. One example of this is Nissan Mexico’s Aguascalientes A1 Plant, which has manufactured 500,000 vehicles through the use of clean energies, making it the first automotive company in Mexico, as well as the first manufacturing facility of the Renault-Nissan Alliance, to achieve this milestone. Through the use of renewable energy, Nissan Mexicana has prevented 152,800 tons of CO2 from entering the atmosphere, and has so far assembled 460,000 vehicles with wind power and 57,400 vehicles with biogas power from the city’s landfills. In all, the use of clean energies accounted for an astounding 68 percent of the production at the Aguascalientes A1 Plant.
The Nissan Energy Saving Collaboration (NESCO) conducts annual surveys (starting 2003 in Japan and 2013 in Europe, Mexico and China) to measure energy loss at Nissan plants in order to develop ongoing new energy-saving countermeasures. NESCO specializes in controlling energy consumption, and diagnoses and visualizes energy flow and its inefficiencies. For example, NESCO studies iron forging, casting and paint shops, then proposes measures to plant management on how to prevent energy loss. In fiscal year 2014, NESCO proposed solutions to reduce CO2 emissions by 50,000 tons.
NESCO has also been used at five Renault and Alliance plants, including AVTOVAZ, UAG and RSM, which have already seen excellent results. NESCO’s area of focus will expand to include waste water loss and waste reduction, in addition to energy loss and CO2 reduction.
Zero emission vehicle penetration
Nissan is improving sustainable mobility through the widespread use of zero emission vehicles. The Nissan LEAF electric vehicle has the ability to safely and conveniently supply electricity stored within its high-capacity lithium-ion batteries to a home through the LEAF to Home power supply system. In addition, Nissan’s “No Charge to Charge” program in the United States provides free access to selected charging stations for two years with the lease or purchase of a new Nissan LEAF in numerous cities including Los Angeles, Portland, San Francisco and Seattle.
In 2014, the company further expanded zero-emission mobility with the introduction of the e-NV200 in the European and Japanese markets. The versatile e-NV200, like the LEAF, has the potential to be used as a mobile power source. In China, the Dongfeng Nissan Passenger Vehicle Company, a division of Nissan’s joint venture with Dongfeng Motor Company, launched the Venucia e30 electric vehicle that offers Chinese consumers a fun-to-drive and reliable EV with very affordable operating costs.
The Nissan Green Program 2016 (NGP2016), launched in fiscal year 2011, is guiding Nissan’s efforts to reduce the company’s environmental impact and resource consumption from global corporate activities while advancing ecological harmony. The company is dedicated to improving in four main areas: zero-emission vehicle penetration, fuel-efficient vehicle expansion, corporate carbon footprint minimization and new natural resource use minimization.
Share:
ADD TO EYE OF Riyadh
MOST POPULAR
KAOUN International and MODON Announce WAM Saudi Expo 2025: Catalysing Saudi Arabia's Industrial Future
Monday 11 November, 2024 1:17Latifa bint Mohammed honours design pioneers shaping Dubai’s thriving creative ecosystem
Tuesday 12 November, 2024 10:18du wins Organisation of the Year for Youth Empowerment in GCC GOV HR & Youth Awards 2024
Monday 11 November, 2024 1:37Johns Hopkins Aramco Healthcare (JHAH) Receives Highest Certification for Excellence in Person-Centered Care from Planetree
Tuesday 12 November, 2024 8:00UNRELIABLE TECH IS RUINING KEY LIFE EVENTS AS 76% OF ADULTS ADMIT TO EXPERIENCING A ‘TECH FAIL’
Monday 11 November, 2024 10:53 ×